Paediatric Dentistry
About the speciality of Paediatric Dentistry
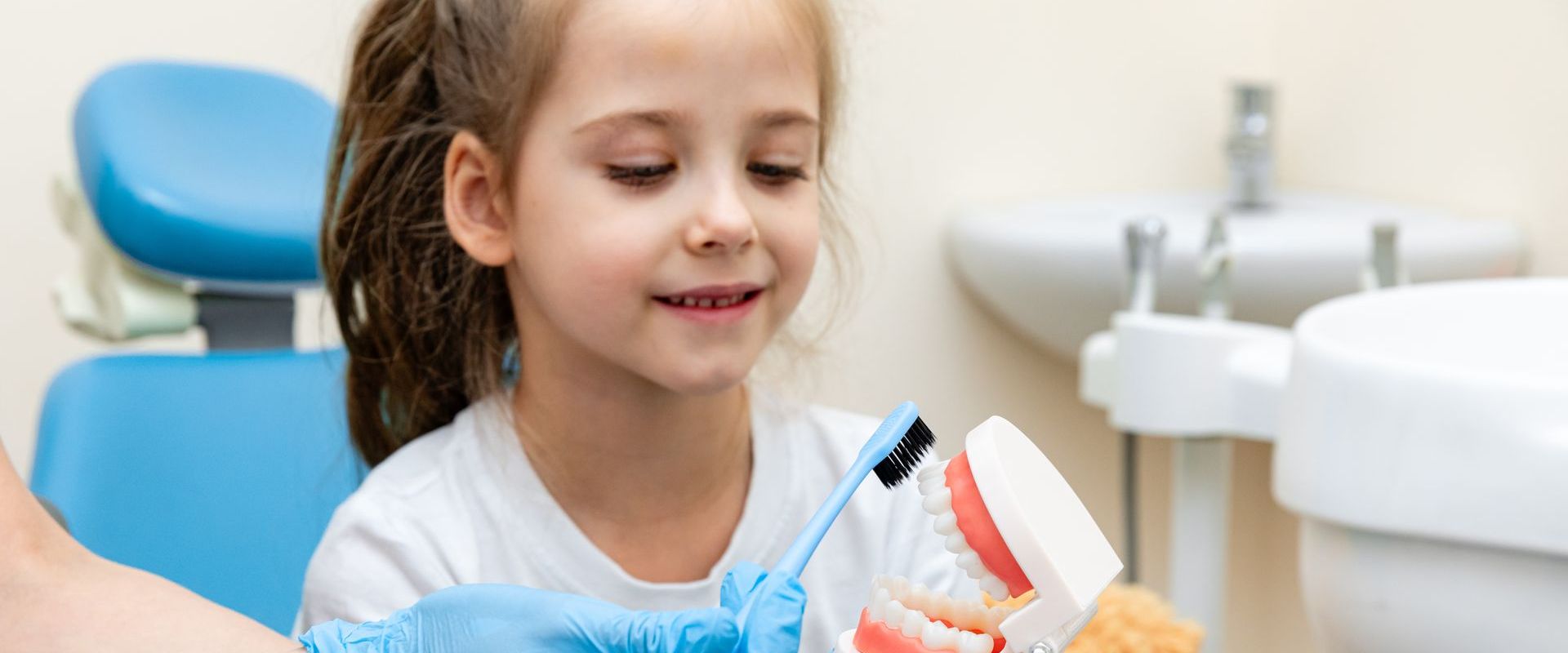
Paediatric dentistry: dedicated to maintaining the oral health of children, adolescents and patients with special needs
Paediatric dentistry is the speciality of dentistry exclusively dedicated to maintaining the oral health of children, adolescents and patients with special needs.
The paediatric dentist works to prevent oral pathology, since monitoring the development of the so-called ‘milk teeth’ is essential not only to ensure correct phonetic and chewing functions but also, and above all, to diagnose and prevent potential problems early on, guaranteeing a healthy final set of teeth.

Paediatric dentists are trained to deal with the specific needs of children, using approaches that make visits to the dentist more pleasant and welcoming.
Benefits of Paediatric Dentistry for oral health
Prevention of dental problems
Paediatric dentistry focuses on prevention, offering guidance on oral hygiene and healthy diets.
Personalised Treatment
All treatments are carried out taking into account the specificities of the age groups in question: smaller body and oral dimensions, growing skull and jaw bones, dynamic eruption process of the dentition and the presence of milk teeth, among others.
Oral health education
In addition to treatment, the paediatric dentist educates children and parents about the importance of oral health and how to maintain it.
Monitoring dental development
Diagnosis and treatment of anomalies in the development of the teeth and jaws.
What pathologies can it treat?

Tooth decay
Frequent sugar intake combined with poor brushing often results in the appearance of tooth decay. If left untreated, tooth decay can lead to the early loss of baby teeth, often with consequences for the positioning and alignment of permanent teeth. In addition to treatment, during the consultation the child and parents are counselled on healthy eating habits and oral hygiene.

Malocclusion
Early identification of alignment and bite problems and functional jaw orthopaedic treatment or referral to orthodontics if necessary.

Enamel Defects
Enamel defects are a risk factor for tooth decay and require specific dental treatment. Among the most common enamel defects is Incisor-Molar Hypomineralisation. Teeth with this type of enamel defect are more fragile and show white or brownish spots, or even rough depressions that increase the risk of caries. Children with this problem are more sensitive to thermal stimuli and find it more difficult to achieve effective anaesthesia during dental treatment, sometimes requiring the use of other behavioural control techniques by the paediatric dentist, such as conscious sedation with nitrogen protoxide.

Dental trauma
Emergency care for fractured, dislocated or avulsed teeth due to falls or accidents.
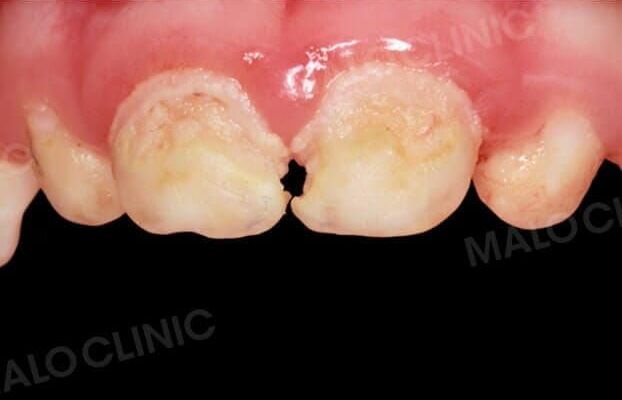
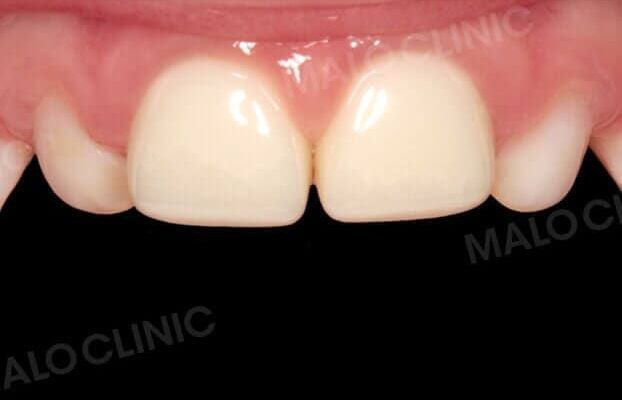
Clinical Cases
Paediatric crowns in zirconia
Our Clinical Team is here to help you!
Clinical Team
FAQ's
1. What to expect at the first paediatric dentist appointment?
Your child's first visit to the paediatric dentist is one of the most important appointments your child has with us, if not the most important. At this appointment, the child gets to know the space, the instruments and the paediatric dentistry team.
The paediatric dentist carries out an assessment of the child's risk of tooth decay, covering the topics of eating and brushing, which are fundamental for maintaining good oral health. Cleaning and the application of topical fluoride are also carried out, as well as intraoral X-rays, if necessary. Paediatric dentistry appointments last an average of 15 to 30 minutes.
At the end of the paediatric dentistry appointment, the diagnosis is explained to the parents and the treatment plan is established.
In the absence of oral pathology, the child should visit the dentist at least every 6 months for a routine check-up, which includes oral cleaning and topical fluoride application.
2. When should I take my child to the paediatric dentist for the first time?
It is recommended to take your child to the paediatric dentist when their first tooth appears, or at the latest by their first birthday.
3. Do milk teeth really need special care, as they will eventually fall out?
Yes, milk teeth are important for chewing, speaking and maintaining space for permanent teeth. Looking after them is essential for the child's future oral health.
4. What should I do if my child is afraid of going to the dentist?
The paediatric dentist has specific training to deal with children's fear and anxiety, turning the visit to the dentist into a positive and pleasant experience.
Through appropriate language suited to the child's age, positive reinforcement, explaining all the steps of the appointment beforehand, among other techniques, it is possible to establish a path of communication between the paediatric dentist and the child, calming them down.
If basic behaviour control techniques are not enough to reassure the child, other solutions can be used.
At MAL O CLINIC we offer the technique of conscious sedation by inhalation of nitrogen protoxide and oxygen, aimed at patients with mild to moderate anxiety. For patients with severe anxiety there is the possibility of carrying out dental treatments under other types of sedation. Our paediatric dentists have extensive experience in carrying out these treatments.
5. What is topical sealant application and why is it important?
To prevent the appearance of caries lesions, fissure sealants are often applied at paediatric dentistry appointments. Sealant is a varnish that, when applied to healthy teeth, protects the chewing surface and prevents the appearance of cavities. Sealing teeth is not universal and is indicated in specific cases to be assessed by the paediatric dentist.
6. How can I prevent cavities in my child?
Encourage good oral hygiene from an early age, including brushing with toothpaste with the right fluoride concentration for the child's age and flossing. Avoid excessive sugar consumption and make regular visits to the paediatric dentist for check-ups and fluoride application.










